
Dynamic Endpoints in Mock Servers: How It Works
Dynamic endpoints in mock servers let you test APIs by tailoring responses based on request parameters. Unlike static endpoints, which provide fixed responses, dynamic endpoints adapt to requests, making them ideal for testing edge cases, simulating real-world scenarios, and speeding up development.
Key Benefits:
- Custom Responses: Adjust based on headers, query parameters, or body content.
- Error Simulation: Test how apps handle invalid inputs or edge cases.
- Independent Development: No need to rely on live APIs.
- Faster Debugging: Create controlled scenarios to identify issues.
Quick Overview:
| Feature | Static Endpoints | Dynamic Endpoints |
|---|---|---|
| Response Type | Fixed | Variable, context-based |
| Request Handling | Ignores parameters | Considers parameters & headers |
| Use Cases | Simple API mocking | Advanced scenario testing |
| Maintenance | Manual updates needed | Adjusts automatically |
How It Works: Dynamic endpoints process headers, query parameters, and body content to generate responses using rules like validation, state simulation, and error handling. Tools like ReqRes make this process easier by allowing you to configure, test, and debug endpoints efficiently.
Dynamic endpoints are essential for better testing and faster development. Ready to try them? Start with tools like ReqRes to streamline your API testing process.
Dynamic Endpoint Mechanics
Dynamic endpoints handle requests and generate responses based on predefined rules, making them essential for effective API mocking.
Request Parameter Processing
Dynamic endpoints analyze three key components of a request to determine the appropriate response:
| Request Component | Processing Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Headers | Pattern matching | Validates authentication and manages content negotiation |
| Query Parameters | Value extraction | Handles filters and pagination settings |
| Body Content | JSON/XML parsing | Validates data and enables conditional responses |
The information extracted from these elements feeds into a decision tree that determines the response.
Response Logic and Rules
Responses are generated using a structured decision tree informed by the processed parameters. The main elements of this logic include:
- Parameter validation: Ensures required fields are present and formatted correctly.
- State simulation: Maintains mock data consistency across multiple requests.
- Error handling: Produces error responses for invalid or incomplete inputs.
- Success responses: Delivers properly formatted data for valid requests.
This approach mimics real-world API behavior, ensuring accurate and reliable testing scenarios.
Default Response Handling
When a request doesn’t match specific criteria, default response handling kicks in to maintain stability. This ensures the testing environment remains functional and predictable.
The fallback process prioritizes the following steps:
- Pattern matching: Attempts to match the request against defined rules.
- Fallback responses: Returns pre-configured default responses for unmatched requests.
- Live forwarding: Optionally forwards requests to actual endpoints, if available.
Developers can use local file mapping to quickly adjust default responses. These fallback mechanisms provide consistency and prevent disruptions during testing.
Creating Dynamic Endpoints
Endpoint Configuration Steps
Setting up request rules and response patterns is key to building dynamic endpoints.
| Configuration Element | Purpose | Example Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Base Path | Specifies the root URL | /api/v1/users |
| HTTP Methods | Defines allowed operations | GET, POST, PUT, DELETE |
| Required Parameters | Lists fields that must be included | user_id, auth_token |
| Optional Parameters | Specifies additional, non-mandatory fields | filter, sort, page |
Response Setup Guide
Start by creating base templates for common HTTP status codes, then tailor them based on the request parameters.
Key components for setting up responses:
1. Status Code Configuration
Set up appropriate HTTP status codes to match different scenarios. Include headers and body templates that align with your API documentation.
2. Dynamic Data Mapping
Use ReqRes's Map Local Tool to link specific request patterns to local files, making it easier to manage dynamic responses.
3. Content Type Handling
Ensure response headers clearly define the content type and other relevant details:
{
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Cache-Control": "no-cache",
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*"
}
Once everything is configured, test the endpoints to ensure they work as expected.
Endpoint Testing Methods
After setting up responses, thorough testing is critical to verify endpoint behavior. ReqRes provides tools for testing directly within its macOS interface.
Testing should include:
- Validation of required and optional parameters
- Error response formatting
- Success response accuracy
- Proper handling of headers
- Simulating varied response times for different scenarios
"ReqRes is a highly efficient, native macOS app to monitor, debug, and mock HTTP(S) requests and responses." - ReqResapp.com
Leverage ReqRes's Map Local Tool to switch between different response scenarios without altering server-side code. Test edge cases such as:
- Missing required parameters
- Invalid authentication tokens
- Incorrectly formatted request bodies
- Rate limiting situations
- Network timeouts
Advanced Implementation Tips
Building on the mechanics of dynamic endpoints, these tips can further improve your API testing process.
Network Condition Testing
Simulate different network scenarios to test how your application performs under challenging conditions. Adjusting delays, bandwidth, and other parameters can help you identify potential issues.
| Network Condition | Configuration Approach | Testing Objective |
|---|---|---|
| High Latency | Add 2–3 second delays | Simulate mobile networks or international traffic |
| Bandwidth Limits | Throttle response size | Test behavior with limited connectivity |
| Connection Drops | Timeout responses | Check app recovery during lost connections |
| Packet Loss | Intermittent failures | Evaluate handling of unstable networks |
Tools like ReqRes allow you to fine-tune response timing to introduce delays and mimic network latency. This approach helps you analyze how your app behaves in less-than-ideal conditions. Besides network simulations, creating realistic data is equally important.
Mock Data Generation
Create realistic test data using templates that align with your API schema. For example:
{
"timestamp": "{{current_timestamp}}",
"user_id": "{{request.params.id}}",
"data": {
"status": "{{random.status}}",
"response_time": "{{network.latency}}"
}
}
Incorporate dynamic tokens, such as the current timestamp or user ID, that adjust based on each request. You can also add logic to modify response data depending on specific testing needs.
Context-Based Responses
Dynamic endpoints can adapt responses based on the request context, such as parameters, app states, or specific edge cases. This builds on the earlier concept of dynamic endpoint logic. Here's an example:
{
"authenticated": {
"status": 200,
"data": { "access_level": "full" }
},
"unauthorized": {
"status": 401,
"error": "Authentication required"
}
}
With tools like ReqRes, you can monitor how your application reacts to these scenarios in real time. This approach ensures your API handles both expected and unexpected conditions effectively.
ReqRes Dynamic Endpoint Tools
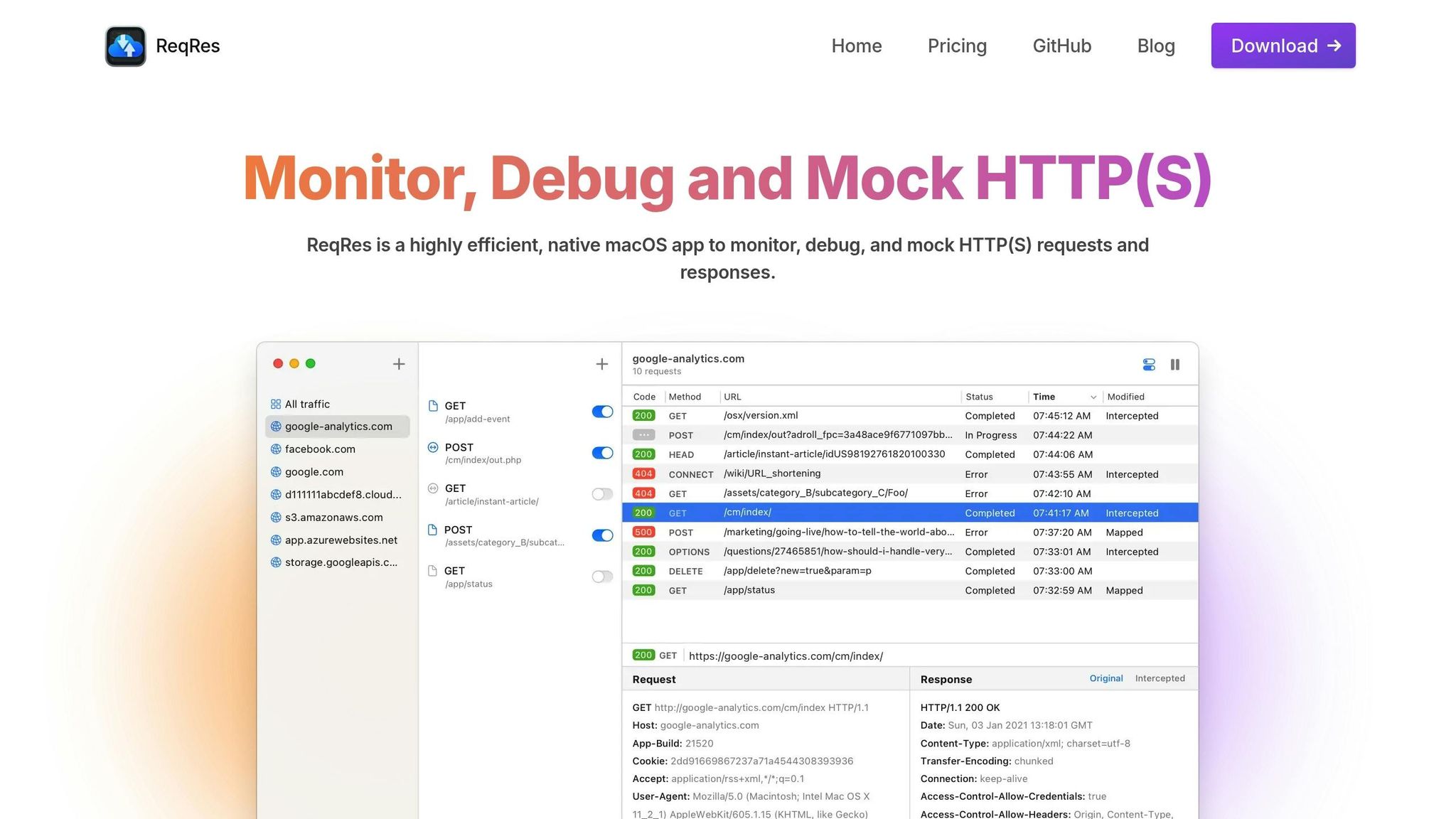
ReqRes simplifies managing dynamic endpoints, making API testing more efficient and accurate.
Core Features of ReqRes
ReqRes helps developers monitor and debug HTTP(S) traffic by intercepting and displaying it in plain text. This makes identifying issues and improving workflows much easier.
| Feature | What It Does | How It Helps Developers |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Monitoring | Shows real-time HTTP(S) traffic | Provides instant debugging insights |
| Server Mocking | Simulates endpoints or servers | Allows development without relying on APIs |
| Local Response Mapping | Uses local files for responses | Speeds up testing and iteration |
How to Set Up ReqRes Endpoints
With ReqRes's Map Local Tool, creating dynamic endpoints using local files is straightforward:
- Define request rules, including URLs, methods, and headers.
- Set up response templates with local files, adding dynamic elements like status codes, headers, or content variations.
- Enable traffic interception to monitor requests and provide instant responses.
This setup fits seamlessly into development workflows, making processes faster and more flexible.
Integrating ReqRes into Development
ReqRes is a handy tool for continuing development without live APIs. It lets you test edge cases using local response files and monitor HTTP(S) traffic in real time. The Map Local feature also allows you to tweak responses quickly without deploying changes to a server.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Dynamic endpoints play a crucial role in API testing today. They allow developers to simulate API behaviors before deployment, cutting down on development delays and making testing more efficient.
| Benefit | How It Helps Development |
|---|---|
| Rapid Iteration | Enables quick updates to response data without changing the server |
| Comprehensive Testing | Makes it easier to test edge cases and different response scenarios |
Ready to implement dynamic endpoints? Here's a quick guide for using ReqRes.
How to Get Started with Dynamic Endpoints in ReqRes
Follow these steps to set up dynamic endpoints with ReqRes:
-
Set Up ReqRes
Start by enabling ReqRes traffic monitoring. This will help you intercept HTTP(S) requests for smoother debugging. -
Configure Responses
Link your local response files to specific endpoints through ReqRes. -
Test Integration
Use ReqRes's real-time HTTP(S) monitoring to integrate endpoints into your workflow and confirm they handle responses as expected.
FAQs
How do dynamic endpoints make API testing more efficient compared to static endpoints?
Dynamic endpoints in mock servers streamline API testing by providing flexibility and adaptability. Unlike static endpoints, they can simulate different scenarios without requiring changes to the server or pre-existing data. This is particularly helpful when the actual API isn’t fully developed or available, allowing developers to continue building and testing without delays.
By enabling on-the-fly customization of responses, dynamic endpoints make it easier to test edge cases, debug issues, and ensure robust application performance - all while saving time and effort during the development process.
How can I set up dynamic endpoints using ReqRes?
Dynamic endpoints in ReqRes allow you to create flexible mock server responses tailored to your API testing needs. While specific steps for setting them up aren’t provided here, the process generally involves defining endpoint paths, configuring request parameters, and specifying dynamic response behaviors. These features are designed to streamline debugging and testing workflows.
For detailed guidance, explore the documentation or in-app resources available in ReqRes to make the most of its dynamic endpoint capabilities.
What are the benefits of using dynamic endpoints to simulate different network conditions during API testing?
Simulating network conditions with dynamic endpoints can significantly enhance API testing by replicating real-world scenarios. This allows developers to see how their APIs perform under varying conditions, such as slow connections, high latency, or intermittent availability.
By using dynamic endpoints, you can:
- Identify potential bottlenecks or failures in your API under specific conditions.
- Test error-handling mechanisms to ensure your application behaves as expected during disruptions.
- Enhance the reliability and user experience of your application by preparing for real-world network challenges.
Dynamic endpoints are an invaluable tool for debugging and refining APIs, helping developers deliver more robust and efficient software.