
Mock Server Configuration: Best Practices for APIs
Mock servers are essential for API testing. They simulate real APIs by providing consistent, predefined responses, enabling faster development, easier testing, and better handling of edge cases. Here’s what you need to know:
- What They Do: Mock servers mimic API behavior without relying on live systems.
- Why They Matter: They help test error scenarios, improve team collaboration, and ensure stable, predictable testing environments.
- How to Set Up: Define endpoints, configure responses, and tailor setups for different environments like development or staging.
- Advanced Techniques: Simulate network delays, error codes, and rate limits. Use stateful interactions to test multi-step workflows.
- Tools: Automate mock generation with tools like Swagger or ReqRes to save time and reduce errors.
- Best Practices: Regularly update mocks, integrate them into CI/CD pipelines, and balance mock testing with real API tests.
Mock servers streamline API testing, making it faster and more reliable. Tools like ReqRes simplify setup and management, making them a great choice for developers.
How to Configure a Mock Server
Setting up a mock server involves defining endpoints, creating tailored responses, and adjusting configurations for different environments. These steps ensure reliable and efficient testing.
Setting Up API Endpoints and Parameters
Start by identifying the key API endpoints you need for testing. Document the expected request-response pairs, including details like HTTP methods, URL patterns, parameters, request body structures, and response status codes. For instance, an endpoint like /users/{userId} should handle dynamic user IDs, while query parameters like ?status=active can filter results.
Mock servers can be configured to return specific responses based on request parameters, mimicking the behavior of dynamic APIs. This makes it easier to test different scenarios without building complex backend logic. When choosing a mocking tool, consider your team's technical expertise, integration requirements, and the level of complexity your project demands. Once selected, set up response patterns to closely replicate real API behaviors.
Setting Up Response Patterns
Your mock server should be able to simulate various HTTP status codes (e.g., 200, 404, 500, 401) and even introduce network delays to test how your application handles less-than-ideal conditions. These delays can mimic real-world scenarios, such as slow server processing times, giving you insights into your app's performance under stress.
To ensure thorough testing, create realistic data structures that match the complexity of production APIs. This includes using nested objects and arrays. Mock APIs can also simulate rate limiting by returning headers and status codes like 429 (Too Many Requests), enabling you to test how your app reacts when hitting API limits.
For added flexibility, customize responses based on parameters, headers, or body content. Advanced tools often allow scripting for dynamic responses that adjust in real time. Some even support stateful interactions, where the mock server retains data from previous requests, making it easier to test workflows involving multiple API calls.
Certain mock services use sophisticated matching algorithms to select the most appropriate response based on the request's path or query parameters. Others offer dynamic templating and rules-based systems to make responses even more realistic.
Environment-Specific Setup
Mock server configurations should be tailored to fit different environments. For example, in development, extensive mocking can allow frontend teams to work independently, while in staging, selective mocking can focus on specific integration tests.
Use environment variables and conditional handlers to adapt mock setups for development, testing, and staging. This eliminates the need for hardcoded URLs, making it easier to transition between environments. Conditional request handlers can also modify responses based on specific parameters, headers, or body content.
To maintain accuracy, regularly update your mock data to reflect changes in the real API. Outdated mocks can lead to false assumptions and integration issues. Many modern tools allow environment-specific configurations using variables, ensuring your mocks stay relevant without constant manual updates. This approach ensures consistency across your testing process and reinforces the reliability of your mock server setup.
Advanced Mock Server Techniques
Advanced mock server strategies can elevate your API testing game, enabling you to simulate real-world conditions and catch issues that basic setups might miss.
Simulating Different Scenarios
Mock servers shine when they mimic unpredictable production environments, helping you test how resilient your application truly is.
Take network latency simulation, for example. By introducing artificial delays, you can test how your app handles slow connections. This is key for validating loading indicators, timeout settings, and error-handling mechanisms, ensuring your app stays responsive even when network performance dips.
Another crucial aspect is error code testing. By configuring your mock server to return various status codes (like 200, 404, or 500), you can see how well your app manages errors. This ensures proper error messages are displayed, and retry mechanisms function as expected.
Rate limiting simulation is another powerful tool. Set up your mock server to simulate API quotas and throttling by returning headers and status codes like "429 Too Many Requests." This allows you to test your app's behavior when it hits usage limits, ensuring retry strategies and error handling are up to par.
For more complex workflows, stateful interactions take things a step further. These allow your mock server to remember previous requests and adjust future responses accordingly. This is particularly useful for testing multi-step processes like user authentication or transactional workflows.
By replicating these scenarios, you can rigorously test your application under controlled conditions, preparing it for the complexities of real-world use.
Performance Testing with Mock Servers
Mock servers aren't just for functional tests - they're also a powerful tool for performance testing, offering controlled environments without relying on external dependencies. They let you simulate API calls at scale to see how your application handles stress.
For instance, load profile testing allows you to simulate different traffic conditions, from steady-state loads to peak traffic spikes. You can test how your app performs under consistent usage, during ramp-up or ramp-down scenarios, and even under heavy loads with delayed responses. This helps pinpoint bottlenecks before they affect users.
Another critical area is failure scenario simulation. By configuring your mock server to mimic service failures, timeouts, or downtime, you can observe how gracefully your app handles unreliable dependencies. These tests reveal weak points in your error management and recovery strategies.
During performance tests, monitor key metrics like latency, throughput, error rates, and resource usage. This gives you a clear picture of how your app behaves under different conditions and highlights areas for improvement.
Using mock servers for load testing also ensures APIs are prepared for high concurrency, slowdowns, and failures - all without impacting production systems. Integrating these tests into your CI/CD pipeline means every code change is evaluated for performance, keeping your app reliable and responsive.
Using Automated Mock Generation
Manually creating and maintaining mock servers can become a chore as APIs grow more complex. This is where automation steps in, making the process faster and more efficient.
Specification-based generation uses tools like Swagger or OpenAPI to automatically create mock endpoints based on your API specs. This ensures your mocks stay aligned with your documented API behavior and saves you from tedious manual updates.
Meanwhile, traffic-based generation captures real-world usage patterns, including edge cases you might not think of during manual test design. By recording actual API interactions, you can create highly accurate test scenarios that reflect real user behavior.
Automated mock generation not only cuts down on manual effort but also improves test coverage by uncovering unexpected interaction patterns.
"Mock API servers streamline software development by simulating real-world APIs, enabling faster testing, efficient error handling, and improved team collaboration, enhancing API testing workflows." – Speedscale
To keep your mocks reliable, ensure they stay consistent with evolving API specifications. Use version control to track changes, document updates, and facilitate team collaboration. Automate checks to verify that mock data aligns with the latest API updates, reducing the risk of inaccurate testing.
Best Practices for Mock Server Management
Keeping mock servers up-to-date is essential to avoid outdated configurations and misleading test results.
Regular Updates and Maintenance
Mock servers require consistent upkeep to remain useful. Since API specifications often change, mocks must adapt to reflect these updates. Testing against outdated mocks can lead to inaccurate results and wasted effort.
Establish a regular maintenance schedule for your mock servers. Depending on how frequently your APIs evolve, a weekly or bi-weekly review usually works well. During these reviews, remove outdated mocks to ensure your testing environment stays clean and relevant.
Maintain a detailed log that links mocks to their corresponding API versions. This makes it much easier to identify and remove obsolete mocks when necessary.
Rely on your specification file as the single source of truth for both backend and frontend teams. Whether you’re using OpenAPI, GraphQL schemas, or another format, this ensures everyone is aligned on API behavior and minimizes issues caused by mismatched expectations.
Real-time monitoring tools can be a game-changer here. They provide immediate alerts for mock-related issues, allowing you to address problems before they disrupt your development pipeline.
"Your goal is to have every mock you create contribute to your tests' value without adding to your maintenance burden. These best practices ensure that every mock you create (and every one you don't create) does exactly that." - Peter Vogel, Author
Another key step is automating specification updates. Configure your CI system to refresh network snapshots and mock configurations whenever API changes occur. This automation helps you keep pace with evolving APIs without adding manual overhead.
By following these practices, you can ensure your mock servers remain a reliable part of your testing strategy.
Balancing Mocking and Real API Testing
Achieving the right mix of mock and real API testing is crucial for effective workflows. Over-reliance on either can create blind spots in your testing process.
Mocks are especially useful in the early stages of development, offering controlled environments to simulate API behavior. On the other hand, real API testing is essential for validating full system integration. It helps catch issues that mocks might miss, such as authentication problems, rate limiting, or unexpected response variations. Always use real API tests for final validation before production.
To get the best results, create detailed test cases covering positive, negative, and edge scenarios. Pair these with contract testing to verify that your mocks accurately reflect real API behavior. Contract testing compares mock responses to actual API contracts, helping you catch discrepancies before they cause issues.
"API mocking enables front-end and back-end developers to work simultaneously. While the back-end team develops the actual API, the front-end team can use a mock API to build and test their interface. This parallel development approach significantly speeds up the project timeline." - Abhishek Sachan, Growth Engineer, Requestly
A hybrid approach - combining mocks for speed and control during development with real API tests for accuracy - ensures your application functions as intended in both simulated and real-world conditions.
Adding Mocks to CI/CD Pipelines
Incorporating mock tests into your CI/CD pipeline takes these practices a step further by automating and streamlining deployments.
Make mock servers a standard component of your CI/CD process. Use tools like Postman or custom scripts to automate response validation. This ensures your application handles both expected and unexpected API behaviors correctly, catching potential issues early in the development cycle.
Go beyond basic mocks by creating enriched ones that simulate complex scenarios, such as high traffic or specific error conditions. These advanced mocks allow for performance, functional, and security testing as part of your automated deployment process, providing more thorough coverage.
To keep everything synchronized, configure your pipeline to automatically update mock configurations whenever API specifications change. This eliminates the need for manual updates and ensures your tests remain accurate.
Finally, design your CI/CD integration with efficiency in mind. Mock servers should start quickly, provide consistent responses, and shut down cleanly to avoid disrupting other pipeline stages or consuming unnecessary resources.
Using ReqRes for Mock Server Configuration
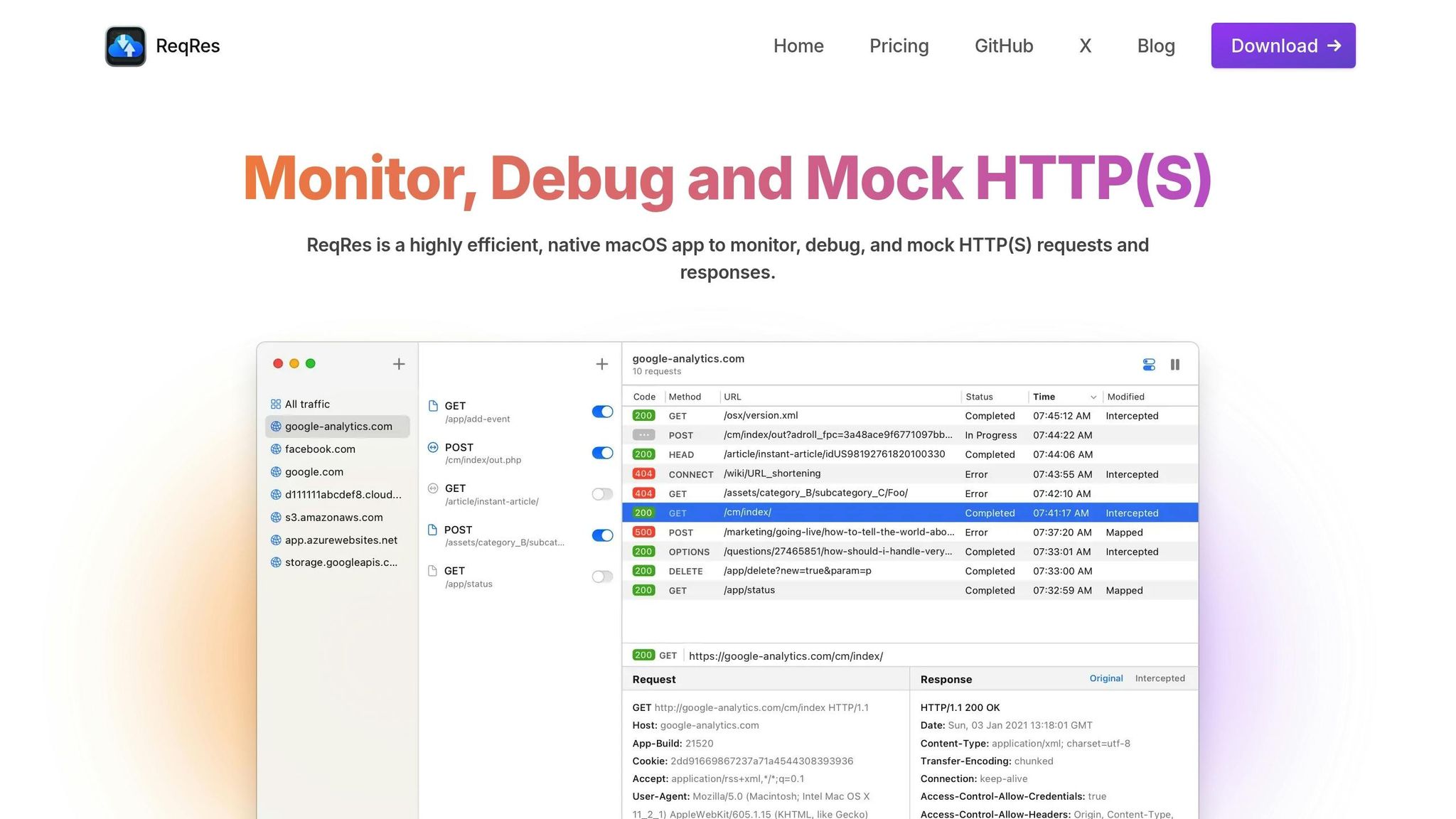
ReqRes is a powerful tool tailored specifically for macOS developers, offering a straightforward way to configure mock servers for API testing. By simplifying what can often be a tedious process, ReqRes makes it easier to manage and test APIs effectively.
Main Features of ReqRes for Mocking
ReqRes stands out with its real-time HTTP(S) monitoring, allowing developers to intercept and analyze network traffic as it happens. This feature provides immediate visibility into API activity, making it easier to spot and address issues.
Another standout capability is request interception, which lets you capture specific HTTP(S) requests and simulate various scenarios without needing to modify your code. It's an efficient way to test different conditions and responses.
One of its most useful tools is the Map Local Tool, which links local files - like JSON or XML - to API endpoints. This means you can use pre-prepared files as mock responses, saving time and enabling you to manage multiple test cases with ease.
ReqRes also eliminates the typical hassle of setting up traffic inspection. You can start monitoring and mocking HTTP(S) traffic right after installation - no need for complex proxy configurations or manually installing certificates. These features not only make testing more reliable but also help streamline the overall development process.
Benefits of Using ReqRes for API Testing
ReqRes solves many of the headaches that come with traditional mock server setups. Its seamless integration with macOS ensures smooth performance without overloading your system.
Switching between live data and predefined mocks is quick and easy, allowing you to test with real-world data when necessary or simulate offline scenarios by simply editing local files. This flexibility is invaluable for testing edge cases or troubleshooting.
The real-time monitoring feature is another game-changer, helping developers identify performance issues or unexpected API behavior that might otherwise be missed.
Getting Started with ReqRes
Getting started with ReqRes is as simple as downloading the app and intercepting your API traffic. Use the Map Local Tool to link your API endpoints with local response files, allowing you to mock responses right away.
Begin by identifying the API endpoints you want to simulate. Monitor your app's network traffic through ReqRes, then create local files with the data you want to return. Whether you’re setting up responses for multiple endpoints or testing different scenarios (like successful responses versus server errors), ReqRes makes the process straightforward.
Additionally, ReqRes integrates seamlessly with testing frameworks and CI/CD pipelines, thanks to its ability to operate at the network level.
The pricing is also reasonable: $59.99 for individual use and $149.99 for teams (up to five devices), both of which include a year of updates and support. This makes it an accessible option for developers looking to enhance their API testing workflows.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Configuring a mock server plays a crucial role in modern API testing. By mimicking real APIs, mock servers streamline development cycles, remove dependencies on third-party services, and create controlled environments for testing edge cases without risking production systems.
Techniques like stateful interactions, automated mock generation, and performance testing elevate basic simulators into powerful tools for verifying API compliance with established specifications. These advanced capabilities enable teams to test more comprehensively and efficiently.
Effective management practices - such as version control, regular updates, and integration with CI/CD pipelines - are essential for maintaining the reliability of mock servers. Automated validation ensures mock responses stay consistent with API specifications, while robust security measures safeguard sensitive data during testing. Together, these practices build a strong framework for dependable quality assurance.
By adopting mock server strategies, teams can shift from traditional API testing methods to a more flexible, efficient approach. Mock servers support independent development, broaden testing coverage, and accelerate feedback loops, paving the way for faster and more reliable software delivery.
For macOS developers, tools like ReqRes simplify the adoption of these strategies. With features like traffic interception, local response mapping, and seamless integration into existing workflows, ReqRes makes advanced API testing accessible and manageable for teams of any size.
FAQs
How can I keep my mock server configurations aligned with frequent API updates?
Keeping your mock server configurations in sync with frequent API updates is crucial for a smooth development process. Start by adopting a versioning strategy - assign version numbers to your APIs to track changes and maintain backward compatibility for existing clients.
Make it a habit to update your mock server regularly to match the latest API specifications. Automating the synchronization between your mock server and live API can be a game-changer, saving time and minimizing errors. This approach ensures that any changes to endpoints, request formats, or response structures are accurately reflected in your mock server.
Collaboration is key. Encourage open communication between development and testing teams to quickly spot and implement updates. Leveraging tools that support automated testing and mock server management can further simplify this process, boosting efficiency in your API development workflow.
What are the advantages of using ReqRes for API testing, and how does it simplify the process?
Using ReqRes for API testing comes with several perks that can speed up the process and simplify your workflow. One standout benefit is the ability to mock API responses without needing a fully developed backend. This means you can test your APIs earlier in the development cycle, catching potential issues before they become bigger problems. It's also incredibly useful for examining edge cases and ensuring your APIs can handle a variety of scenarios.
Another major advantage is real-time monitoring and debugging. With ReqRes, you can instantly intercept and review HTTP(S) requests and responses. This eliminates the need for complicated setups that are often part of traditional debugging methods, saving both time and effort. By streamlining the testing process and delivering instant feedback, ReqRes makes it easier to build APIs that are reliable and efficient - without unnecessary headaches.
How can techniques like stateful interactions and network latency simulation improve API testing?
Advanced Techniques for More Effective API Testing
Techniques like stateful interactions and network latency simulation can take API testing to the next level by mimicking real-world scenarios.
Stateful interactions allow mock servers to "remember" previous requests and responses. This means developers can test workflows that rely on the application's state, such as session management or how the system handles errors. It’s a powerful way to ensure your application behaves as expected in state-dependent situations.
On the other hand, network latency simulation introduces controlled delays to replicate various network conditions. This helps teams see how an application performs under less-than-ideal circumstances, revealing potential bottlenecks or performance issues. It’s a critical step for refining the user experience.
Together, these techniques do more than just improve testing accuracy - they also create a smoother collaboration process between frontend and backend teams. By addressing potential issues early, they can save time and help streamline development workflows.